Oxidized Oligomers from Polyolefins
N. Wolf, S. Säger, M. Lommatzsch, T. J. Simat
Analysis of volatile oxidized oligomers from polyolefins by off-line normal phase high performance liquid chromatography and one-dimensional and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography
2021
Polymer Degradation and Stability
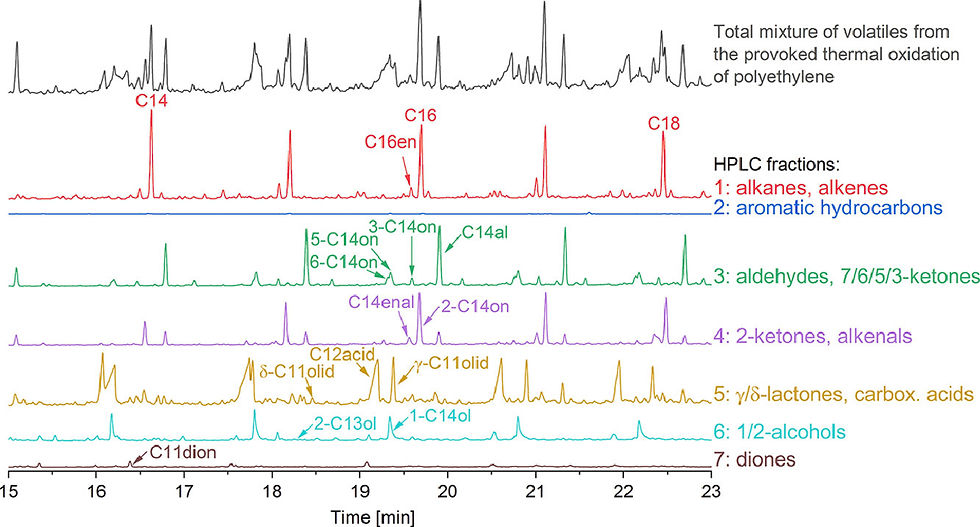
The off-line coupled high performance liquid chromatography - gas chromatography - mass spectrometry (HPLC-GC–MS) was used for the analysis of oxidized oligomers from polyolefins. In order to optimize the HPLC fractionation method, a complex substance mixture of volatile organic compounds (VOC) from the provoked thermal oxidation of polyethylene (PE) was investigated. The fractionation was performed by normal phase HPLC, which separated the analytes according to their polarity. The seven obtained fractions were transferred off-line to the GC–MS. By means of fractionation nearly all coelutions present in the total extract could be avoided, which facilitated the identification of substances considerably. In addition, a separation according to functional moieties of substances was achieved, resulting in homologous series of compounds in the individual fractions: polyolefin oligomeric hydrocarbons (POH) in fraction 1, aldehydes and 7-, 6-, and 5-ketones in fraction 3, 2-ketones and alkenals in fraction 4, lactones and carboxylic acids in fraction 5, 1- and 2-alcohols in fraction 6 and diones in fraction 7, respectively. In this work, 7-, 6- and 5-ketones, δ-lactones, 2-alcohols and diones were identified for the first time in oxidized PE. Verification of fractionation and substance identification was done by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography - time of flight - mass spectrometry (GCxGC-TOF-MS) measurements as well as off-line HPLC-GC–MS measurements using a mixture of reference substances. The fractionation approach was applied for the analysis of a commercial PE film after melt flow extrusion. POH were eluted in fraction 1, while n-aldehydes (with a carbon chain length of C11-18) were identified in fraction 3 and 2-ketones (C13-15) in fraction 4. The amounts of the individual detectable oxidized oligomers were estimated semi-quantitatively to range from 10 – 170 µg/kg.